September 8, 2012, by Jen Alic, in Oilprice.com via CNBC
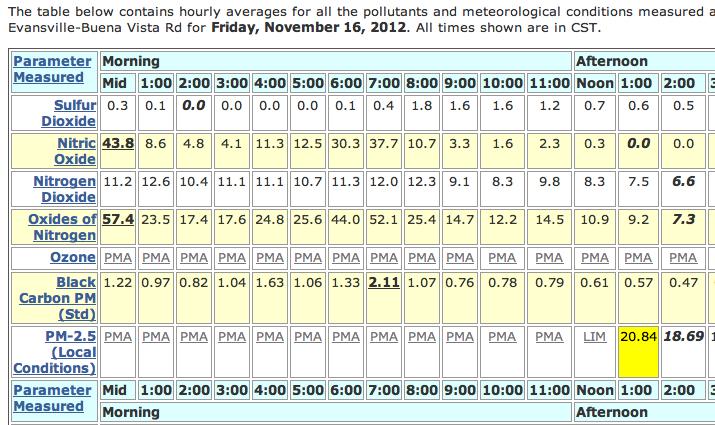
 Half of all industrial toxic air pollution comes from power plants, and 6,700 power plants and heavy industries are responsible for 80 percent of all greenhouse gas emissions in the United States. Coal- and oil-fired power plants contribute 44 percent of all toxic air pollution. Toxic mercury and emissions from the country’s electricity sector are estimated to cause tens of thousands of premature deaths, heart attacks, asthma cases and chronic bronchitis every year.
Half of all industrial toxic air pollution comes from power plants, and 6,700 power plants and heavy industries are responsible for 80 percent of all greenhouse gas emissions in the United States. Coal- and oil-fired power plants contribute 44 percent of all toxic air pollution. Toxic mercury and emissions from the country’s electricity sector are estimated to cause tens of thousands of premature deaths, heart attacks, asthma cases and chronic bronchitis every year.
Many of the US’ most toxic states have seen a reduction of pollution over the past several years, but a federal court of appeals ruling to scrap an EPA regulation on “Cross-State Air Pollution,” designed to reduce air pollution carried from one state to another. Power plants had been expecting this ruling to be approved for over a year, and had adjusted their practices accordingly. The immediate reaction to the federal court’s scrapping of the rule resulted in a queuing up of power plants to abandon preparations for this compliance. Likewise, the EPA’s Mercury and Air Toxics standards (MATs), designed to cut mercury air pollution beginning in 2015 by 79 percent from 2010 levels failed in the Senate in June.
So where are we now? Well, we’re stuck with this list of states that are the most toxic, and while much progress has been made, the list is likely to contain the usual suspects next year and fewer improvements on pollution.
Number 1: Ohio
Ohio’s electricity-generation sector emitted more than 36.4 million pounds of harmful chemicals in 2010, accounting for 62% of state pollution and about 12% of toxic pollution from all US power plants. The state also ranked 2nd in industrial mercury air pollution from power plants, emitting almost 4,210 pounds in 2010 (73 percent of the state’s mercury air pollution and 6 percent of US electricity sector mercury pollution).
Ohio is home to the Gen J M Gavin coal plant in Cheshire, which is the 9th biggest polluter in the United States, according to the EPA, which estimates the plant’s greenhouse gas emissions for 2010 at 16,872,856 CO2e.
Number 2: Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania is ranked third on the second annual “Toxic 20” ranking of states whose residents are exposed to the most pollution from coal- and oil-fired power plants. It represents a small improvement over last year, when Pennsylvania ranked second in the nation in the percentage of toxic pollution generated by power plants. Pennsylvania is responsible for some 10% of all toxic pollution from power plants in the US, releasing nearly 32 million pounds of harmful chemicals in 2010 alone.
From 2009 to 2010, air pollution from all sources in Pennsylvania dropped by 20 percent and from coal-fired power plants by 24 percent, according to HRDC.
Number 3: Florida
While the EPA ranked Florida the 6th worst polluter in 2010, the NRDC ranked it as 2nd worst in its 2012 list. Florida’s electricity-generation sector emitted nearly 16.7 million pounds of harmful chemicals in 2010, according to the EPA, accounting for 57 percent of all state pollution and 5 percent of toxic pollution from all US power plants. Florida’s electricity sector emitted some 1,710 pounds of mercury into the air, accounting for 75 percent of the entire state’s mercury air pollution for that same year.
Florida has undergone a major shift from coal to natural gas. Twelve years ago, natural gas accounted for less than 30 percent of Florida’s electricity production. By 2011, Florida was generating 62 percent of its total power from natural gas, with coal accounting for 23 percent. (Only Texas has a higher percentage.) Florida has three nuclear power plants, which accounted for just under 10 percent of electricity generation in 2011. Florida has 10 large power plants, eight of which are now fueled by natural gas.
However, despite the shift from coal to natural gas, Florida’s carbon dioxide emissions have continued to increase, while sulfur dioxide emissions have been reduced. Florida has seen its greenhouse gas emissions increase from 91 million tons in 1990 to 124 million tons in 2010.
Number 4: Kentucky
Kentucky may not have been ranked the worst overall polluter in the US, but it is ranked worst in terms of toxic air pollution from coal-fired power plants, with HRDC officials specifically citing Kentucky’s poor control over these plants and its failure to adopt any laws or regulations that would lead to a notable reduction in pollution.
Kentucky’s electricity sector actually saw an increase in toxic air pollution from 8.8 million pounds in 2009 to 9.6 million pounds in 2010.
It’s not likely to improve much. Just one day after a federal appeals court scrapped the EPA rule to curb long-distance power plant pollution drifting, the Kentucky-based Big Rivers Electric Cooperative power plant announced it would abandon pollution controls that would have allowed it to comply with the EPA’s regulation.
Number 5: Maryland
Ranked 5th overall for total industrial pollution, coal-burning power plants keep Maryland higher on the pollution list than the state would like. In terms of coal-burning power plant pollution, Maryland is ranked 19th by the NRDC, which also noted that the state’s toxic emissions from power plants dropped by 88 percent over the course of one year. The biggest polluters are the Chesterfield, Chesapeake and Clinch River power plants.
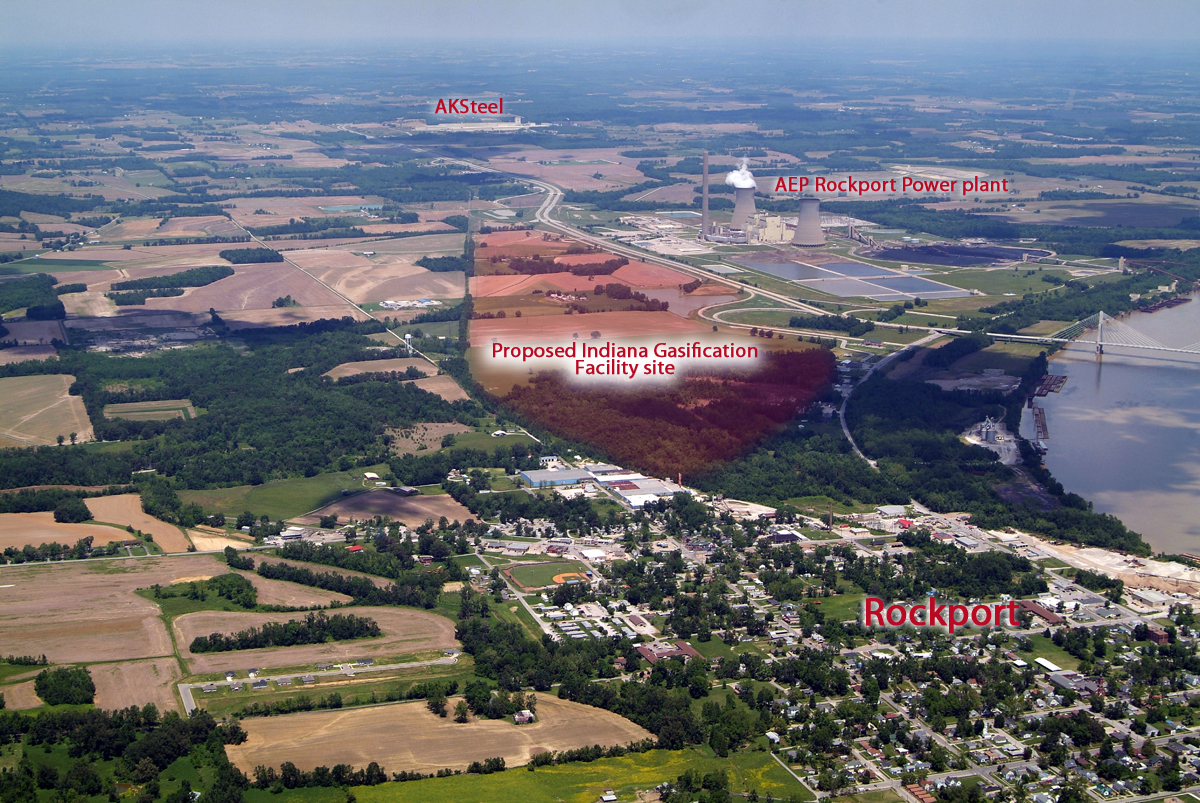
Number 6: Indiana
 The Gibson coal plant in Owensville had total greenhouse gas emissions of 17,993,350 CO2e in 2010, according to the EPA, which ranked the plant the fifth worst polluter in the US. The state’s Rockport coal plant ranked the 10th worth polluter in the country, with total greenhouse gas emissions of 16,666,035 CO2e. Continue reading →
The Gibson coal plant in Owensville had total greenhouse gas emissions of 17,993,350 CO2e in 2010, according to the EPA, which ranked the plant the fifth worst polluter in the US. The state’s Rockport coal plant ranked the 10th worth polluter in the country, with total greenhouse gas emissions of 16,666,035 CO2e. Continue reading →